一、Hydrolysis acidification systembrief introduction
Hydrolysis is the process by which complex, insoluble polymers are converted into simple, soluble monomers or dimers. Due to their large molecular weight, high-molecular organic compounds cannot penetrate cell membranes and thus cannot be directly utilized by bacteria. They are first broken down into smaller molecules through the action of bacterial extracellular enzymes. The most distinctive feature of this stage is that biochemical reactions occur outside cells, where microorganisms release either free extracellular enzymes or immobilized enzymes attached to cell walls to catalyze oxidation reactions (primarily involving macromolecule chain cleavage and solubilization). Acidification, a typical fermentation process known as acidogenic fermentation, involves the biodegradation of organic substrates acting as both electron acceptors and donors. During acidification, soluble organic matter is converted into end products dominated by volatile acids. In mixed microbial systems under anaerobic conditions, hydrolysis and acidification cannot be completely separated even with strictly controlled conditions, because hydrolytic bacteria are essentially fermentative bacteria with hydrolytic capabilities. Hydrolysis is energy-consuming—fermentative bacteria expend energy to hydrolyze substrates for obtaining fermentable water-soluble substances, while generating energy through intracellular biochemical reactions and excreting metabolites (mainly organic acids under anaerobic conditions). When both insoluble and soluble organic matter coexist in wastewater, hydrolysis and acidification proceed simultaneously and inseparably. Excessive pH reduction caused by acidification may inhibit hydrolysis processes.
- Hydrolysis-acidification system composition
The system is mainly divided into: influent system, water distribution system, biological filler system, effluent control system, sludge discharge system, and auxiliary facilities.
- Advantages of hydrolysis-acidification system
- Compared to the traditional hydrolysis process, the sludge-biofilm coupling process has a shorter retention time, reduces tank volume, and lowers civil engineering investment;
- The activated sludge and biofilm coexist, with high system sludge concentration, long sludge age, and high treatment efficiency;
- Uniform water distribution and effective hydraulic mixing;
- Simple structure, convenient operation and maintenance, and low energy consumption;
- Less excess sludge and good sludge properties;
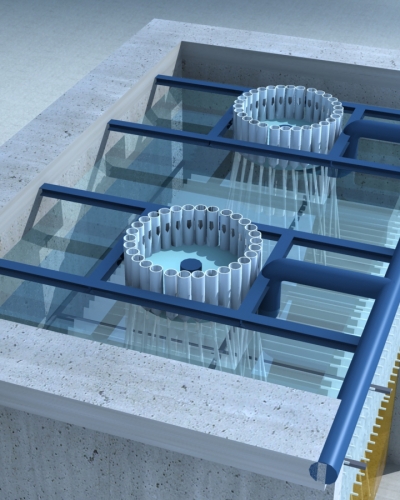
- Core unit of hydrolysis acidification system.
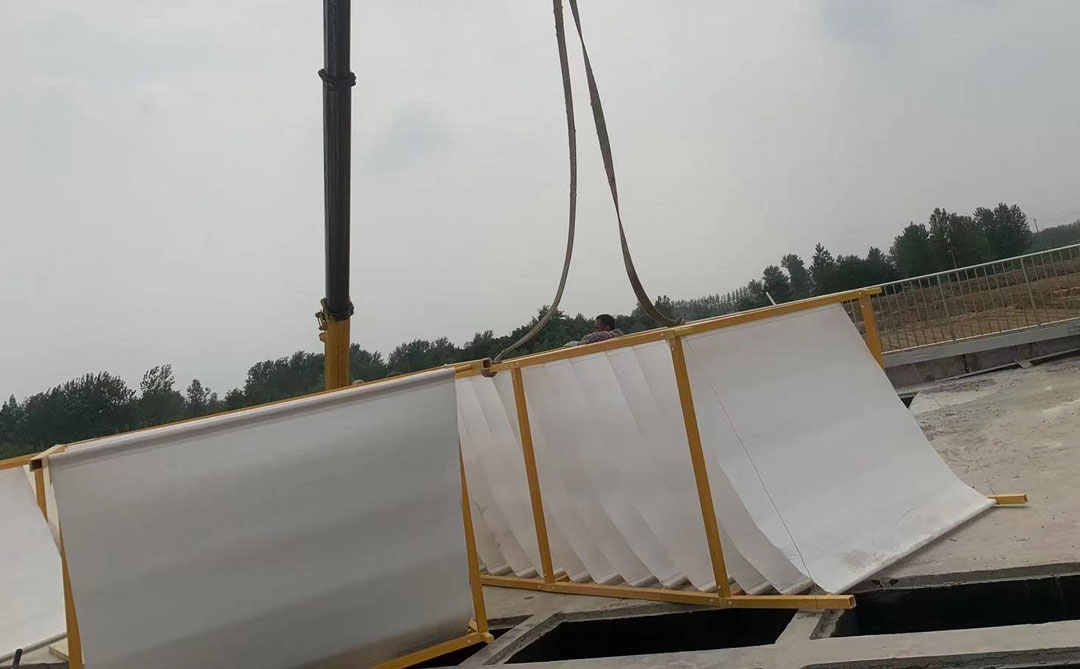
- Water distribution device (multi-point water distributor, pulse water distribution):
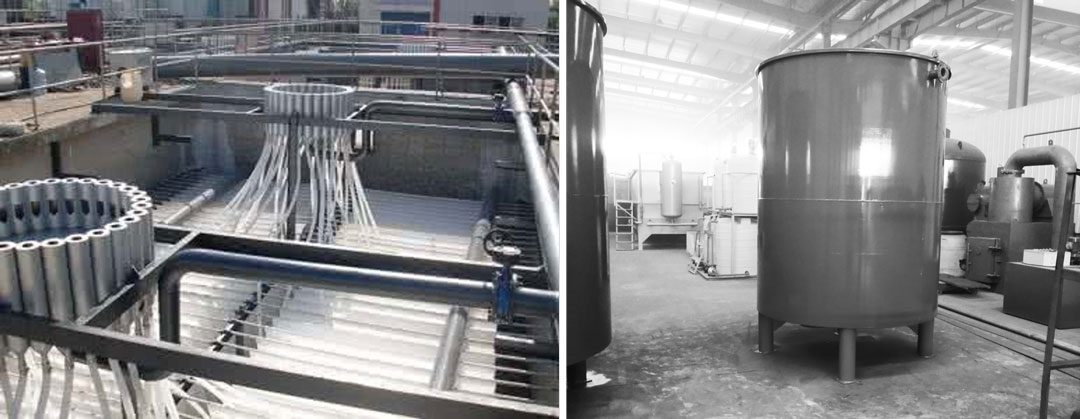

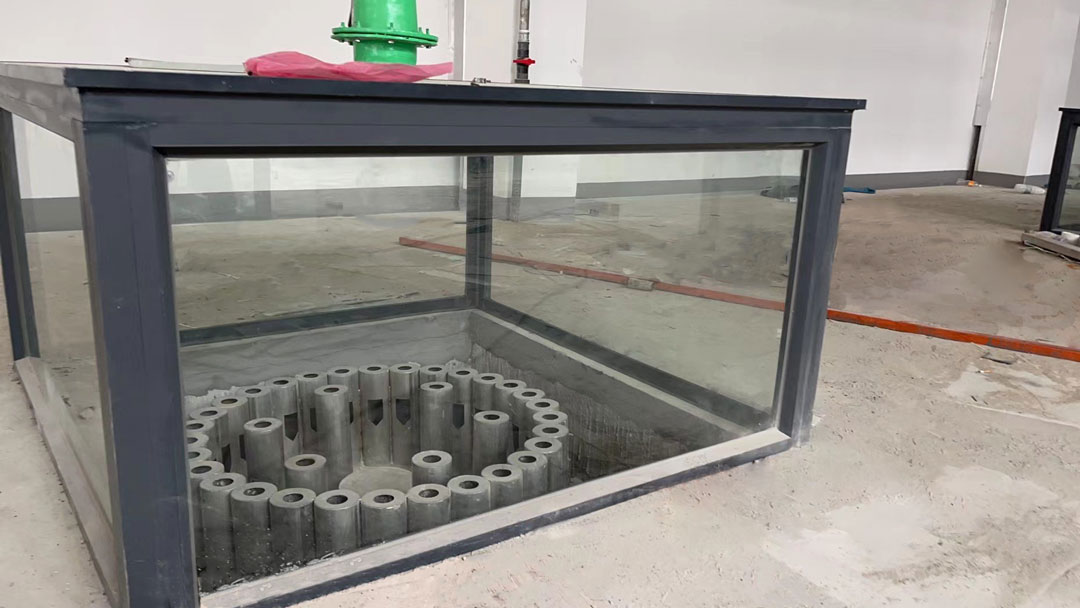
- Biological fillers:





 苏公网安备 32050902101529号
苏公网安备 32050902101529号 Scan WeChat QR to Follow
Scan WeChat QR to Follow